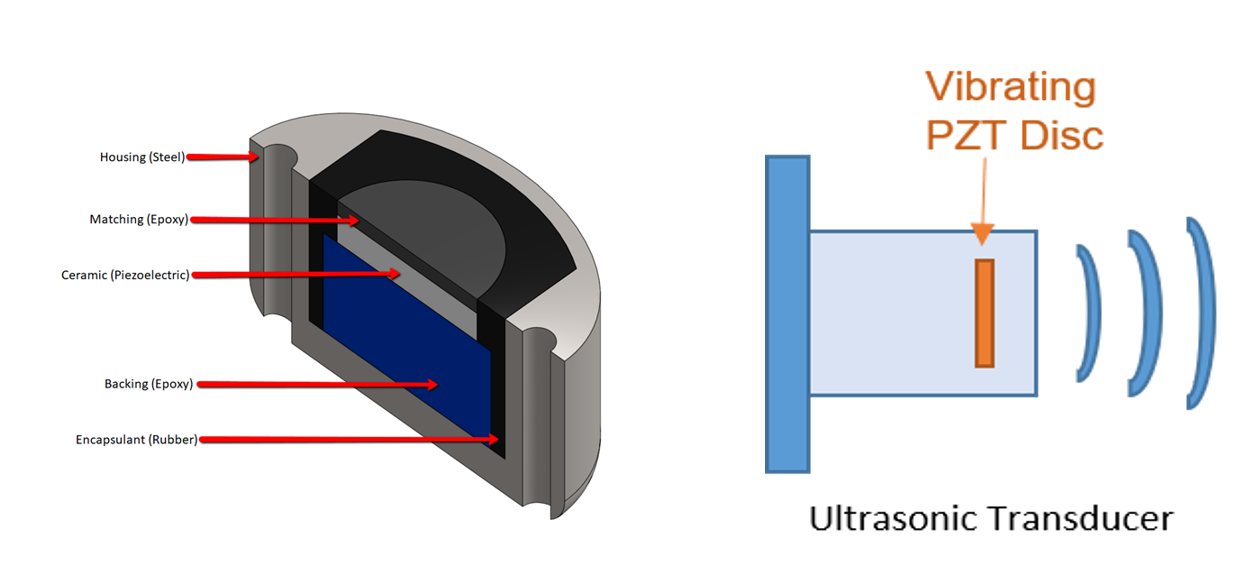
The most “basic” type of device capable of harnessing piezoelectricity is called a PZT Disc.
It’s used in a lot of sensors, electronic filters,… etc
I decided to make a video to teach you how to simulate one with OnScale.
If you don’t have access to YouTube, click here to view the video.
Why OnScale?
Because that the only software capable to handle complex piezo-voltage-acoustic fully coupled models.
Even if other FEA software such as Comsol can do basic stuff. OnScale is more than 10 times faster to simulate this kind of application (Ultrasonic sensors, SAW& BAW Filters, MEMS based devices,… ).
For those interested to know, OnScale has a nonlinear explicit solver which couples electricity, mechanical displacement, stresses and acoustic results and solves all that in a very clever way.
Note also that you can use OnScale for free up to 10 Core/Hour per month.
Just create an account and you can download the software right away!
What will I talk about in this video?
I packed this video with useful knowledge. I am sure you will learn a lot:
- What is a PZT Disc?
- What is PZT Material?
- How is PZT Material Used?
- How to Simulate a PZT Disc in 3D
- Model Definition
- Results we can get
- 3D PZT Disc Step-by-step Tutorial in OnScale
What is a PZT Disc?
It’s a small disc made of a special type of ceramic piezoelectric material called Lead Zirconate Titanate or PZT. If I connect 2 electrodes on both sides of this disc, I can measure the voltage generate by the piezoelectric effect.

Simply said, it generates a voltage when I apply a pressure on the disc. You can also apply a voltage and the disc will then start to vibrate and generate acoustic waves.

What is Lead Zirconate Titanate (PZT)?
Lead zirconate titanate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Pb[ZrxTi1−x]O3 (0≤x≤1). PZT is a ceramic perovskite material that shows a marked piezoelectric effect, meaning that the compound changes shape when an electric field is applied.
It appears as a white powder like in the photo below and can be then shapes into the form of a disc to be used as the main way to generate acoustic waves and vibration in ultrasonic sensors.
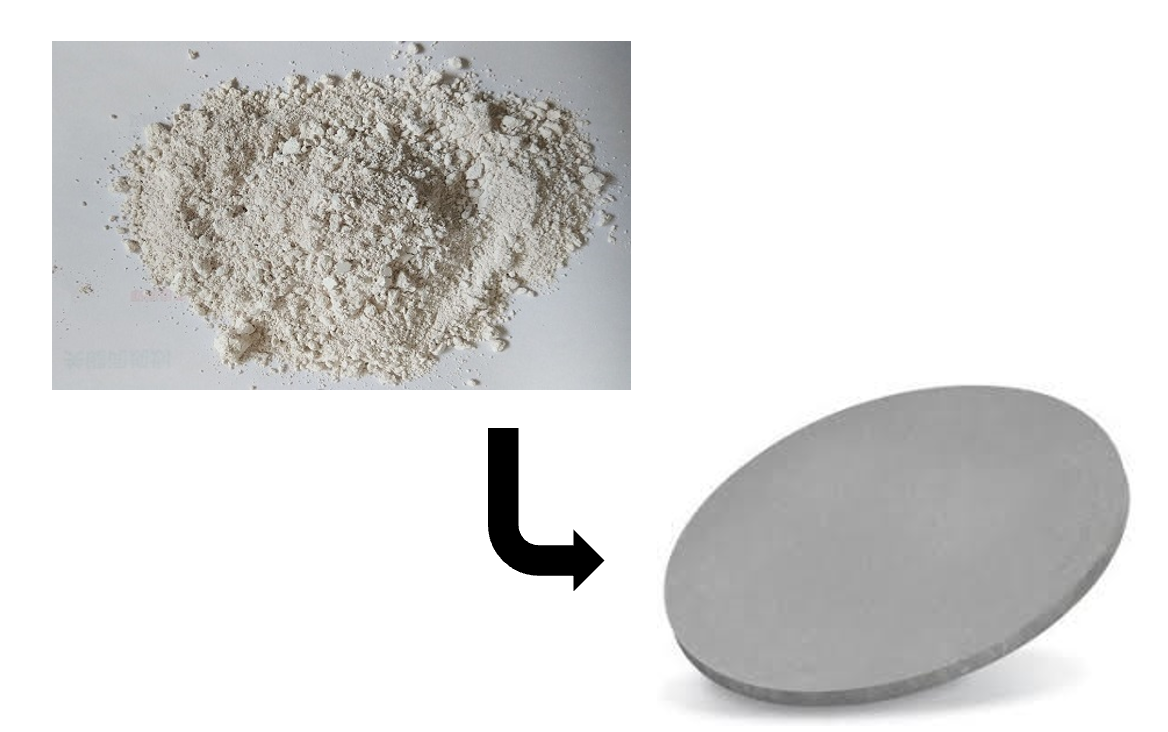

How is PZT Material used?
It is used in a number of practical applications such as ultrasonic transducers and piezoelectric resonators.
Simulating PZT in 3D or 2D?
You will note that in this video, I am showing mainly how to simulate this PZT Disc in 3D, but in fact, it is much better to simulate it as a 2D Axi-symmetric model.
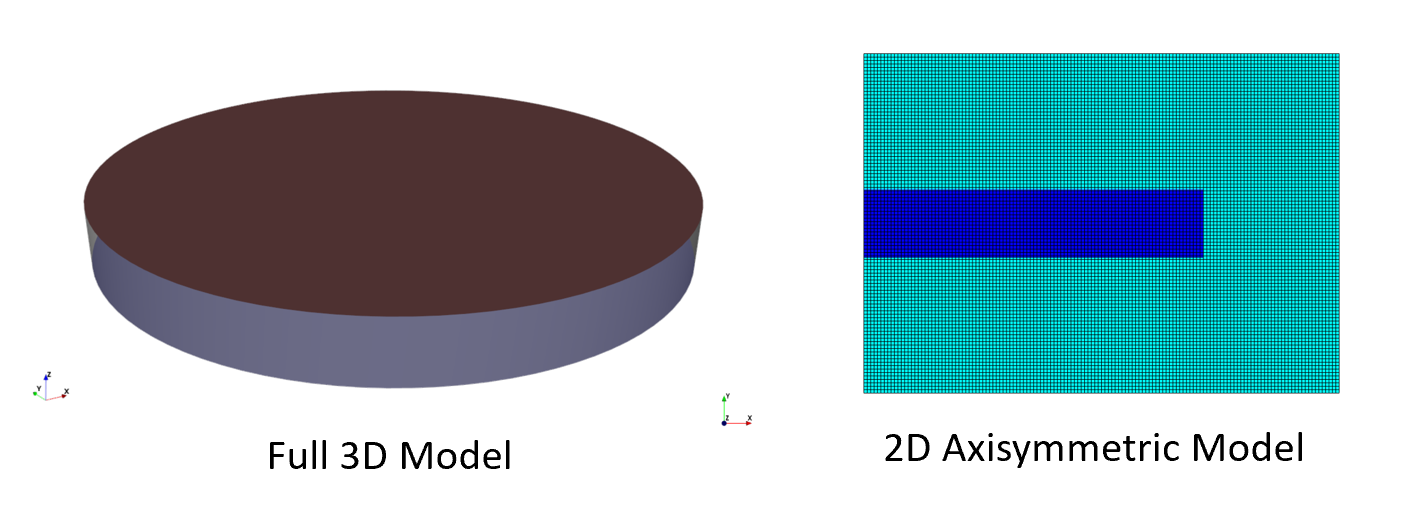
You can consider this tutorial more as an exercise to understand how a PZT Disc works and can be simulated… but keep in mind that whenever you have an axial symmetry, you would rather simulate it as a 2D Axi-symmetric model because that way you save a lot of calculation time for results which are (most of the time) even more accurate!
Model Definition
Here are some characteristics of the model that I created in the video:
- Geometry: PZT CAD Cylinder (Diameter: 20 cm, thickness: 2 cm)
- Unit: m
- Material: CTS 3203HD (pmt3)
- Loads: Time-dependant Voltage applied through 2 electrodes
- Voltage time distribution: Ricker Wavelet of 1 MHz
You can download the CAD here
pztcdisc simulation model definition 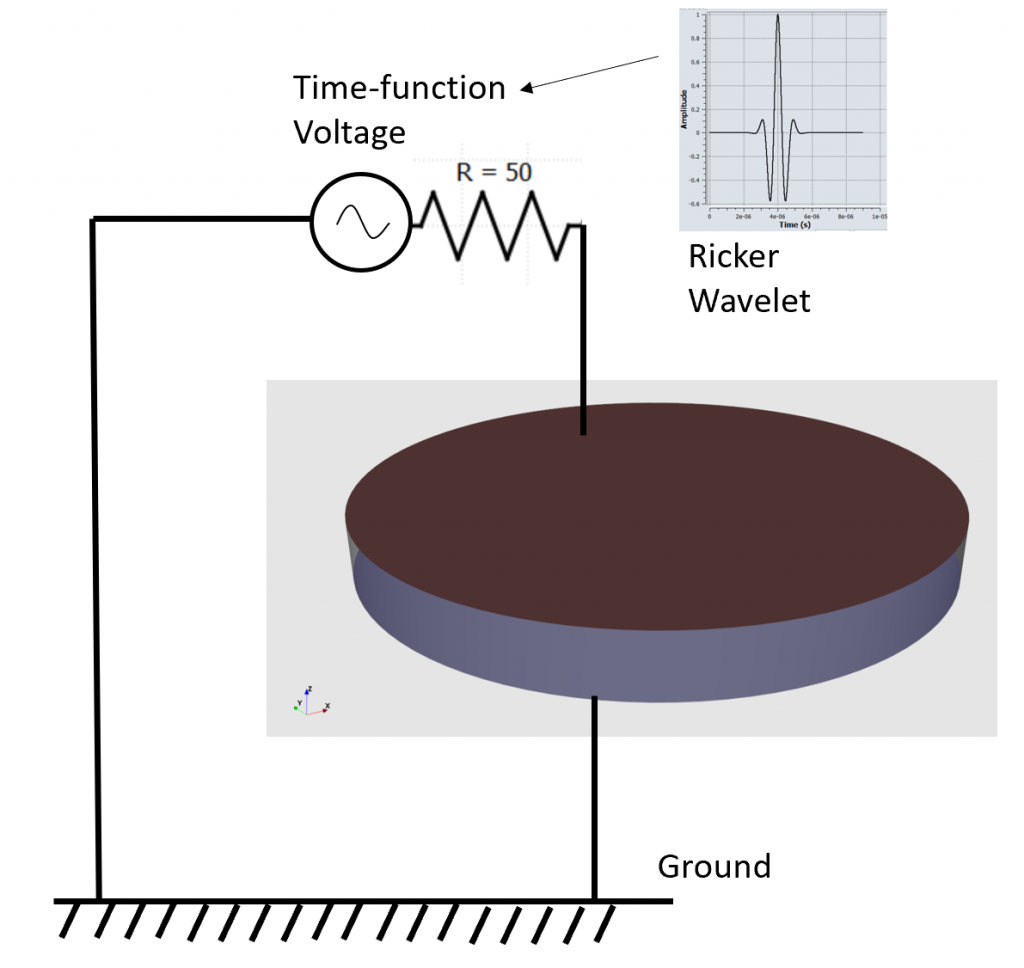
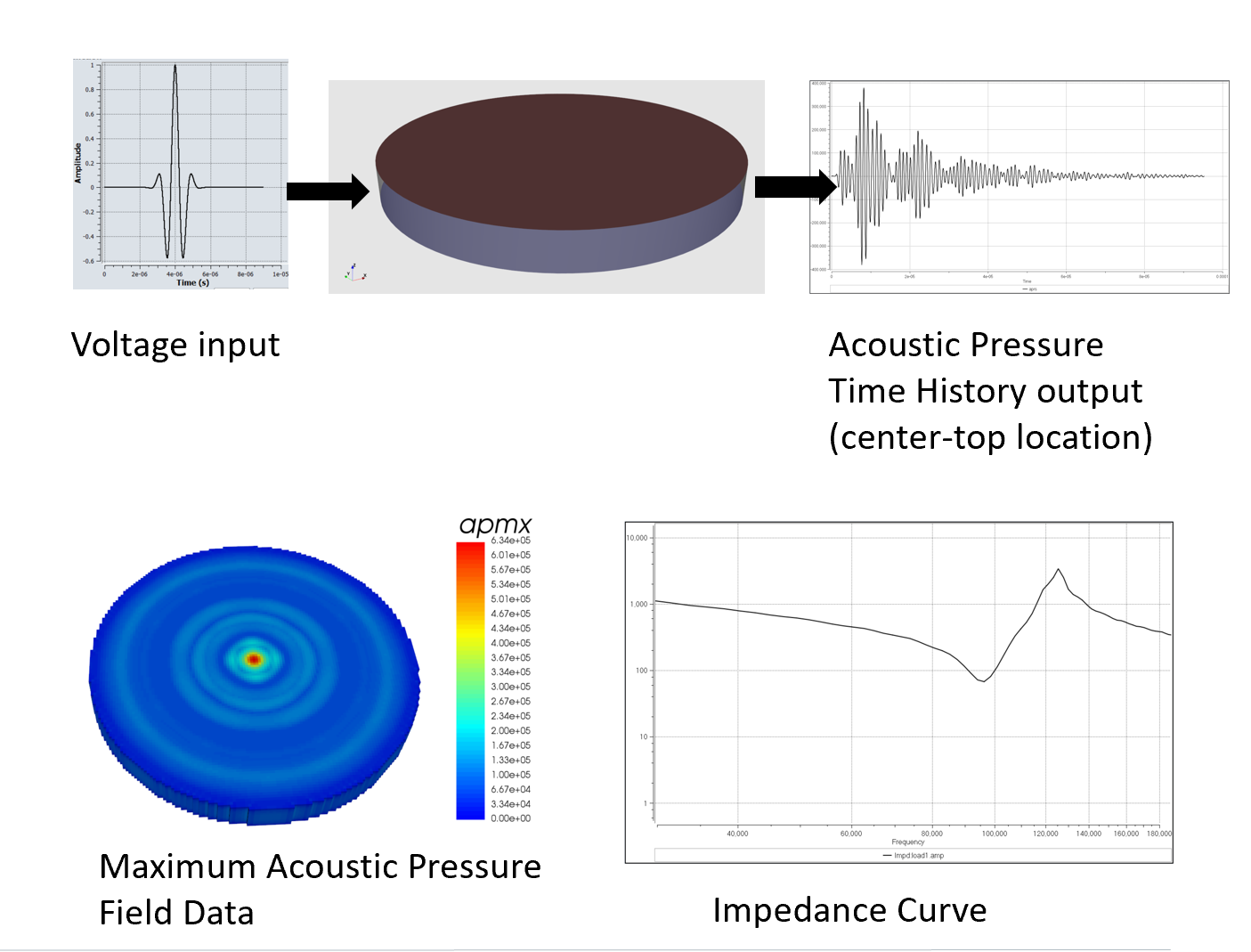
What are the results that you can obtain from this simulation?
- Acoustic Pressure (aprs)
- Maximum Acoustic Pressure (apmx)
- Charge in the electrode
- Impedance Curve
- Mode Shape
Download the model:
Here’s the full model that I built in this video:
Download the 3D PZT Disc OnScale Model
More Material about PZT and PZT Disc Simulation:
If you prefer to read a tutorial fully detailed step by step, you have one available here:
Tutorial: 2D Axi-symmetric PZT Disc in Water Load
This one is also good:
Tutorial: 3D Piezoceramic bloc simulation
Other OnScale tutorials:
I have also made a bunch of other tutorials about OnScale that you can read here:
http://feaforall.com/category/tutorial/onscale-video-tutorial/
If you have any question or comment, just leave it on this page :)
Cyprien “Starting in Piezo Simulation” Rusu

I hope this tutorial was very useful for you!
I want to know which parameter on OnScale determine the first pulse in impedance where is should be, could you help me please?
Hi Rama,
In OnScale, you are doing a time response simulation. The input pulse is a wavelet with a large spectrum of frequencies. That’s why the impedance you get in output is the full impedance curve excited at almost all frequencies. This result is much more realistic because the real world is time domain.
Also, in OnScale, it will be more accurate if you use a 2D axisymmetric model rather than full 3D. Have a look at the PZT Tutorial on the Onscale support website.
Hi Cyprien,
I am working on a project based on the Surface Acoustics Wave (SAW) by a piezo disc. I want a similar simulation,
Would you please help me out? Where and how I can do the simulation?
I am looking forward to hearing from you soon.
Thank you.
In this model volatge is used as an input and the pressure as output, if we want to use pressure applied as an intput and get the voltage as ouptut, what all changes are required ?